even root ,Finding Domain: Radical/Root Function (Even Root),even root, The case of even roots (i.e., when n is even) closely parallels the case of square roots. That’s because when the exponent n is even, the graph of \(y = x^n\) closely resembles that of \(y = x^2\). For example, observe the case . Here, we uncover the evolution of the slot machine, from 1894 to the modern slots of today. That’s right, the origin of slots starts in the 1890s, the later years of the Wild West. As railways and telegraph lines snaked across .
0 · Flexi answers
1 · Even Root Function
2 · Even
3 · Finding Domain: Radical/Root Function (Even Root)
4 · 4.4 Root Functions and Their Transformations
5 · 5.1: Roots and Radicals
6 · Why is the even root of a number always positive?
7 · 5.1 Radical Functions and Radical Expressions
8 · 8.1: Exponents and Roots
9 · Study Guide
10 · Domain of Even Root Functions
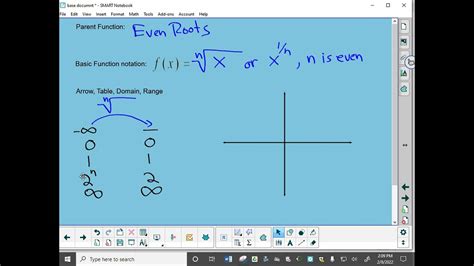
Ang mga root function ay isang mahalagang bahagi ng algebra at calculus, at ang pag-unawa sa iba't ibang uri nito ay kritikal para sa matagumpay na paglutas ng mga mathematical problem. Sa artikulong ito, tututukan natin ang mga even root function, partikular ang square root, at tatalakayin ang kanilang mga katangian, domain, at kung bakit laging positibo ang resulta ng even root ng isang non-negative na numero. Gagamitin natin ang iba't ibang resources tulad ng Flexi Answers, mga materyales mula sa 4.4 Root Functions and Their Transformations, 5.1: Roots and Radicals, 5.1 Radical Functions and Radical Expressions, 8.1: Exponents and Roots, study guides, at iba pa upang magbigay ng komprehensibong gabay.
Ano ang Even Root Function?
Ang even root function ay isang uri ng radical function kung saan ang index ng radical ay isang even number. Ang pinakapamilyar na halimbawa nito ay ang square root, na may index na 2 (bagama't hindi ito karaniwang isinusulat). Ang general form ng isang even root function ay:
f(x) = ⁿ√x
kung saan ang 'n' ay isang even integer (2, 4, 6, 8, atbp.).
Mga Katangian ng Even Root Function:
* Index: Ang index ay palaging isang even number.
* Radicand: Ang expression sa ilalim ng radical sign (x sa pormula sa itaas) ay tinatawag na radicand.
* Domain: Ang domain ng even root function ay limitado. Ang radicand ay dapat na non-negative (mas malaki sa o katumbas ng zero) dahil hindi tayo maaaring kumuha ng even root ng isang negatibong numero sa set ng mga real numbers. Ito ay dahil walang real number na kapag minultiply sa sarili nito ng even number of times ay magbibigay ng negatibong resulta.
* Range: Ang range ng even root function ay karaniwang non-negative din. Ang square root ng isang numero ay palaging positibo o zero.
Bakit Laging Positibo ang Even Root ng isang Non-Negative na Numero?
Ito ay isang mahalagang konsepto na dapat maunawaan. Kapag sinasabi nating "square root of 9," ang tinutukoy natin ay ang principal square root, na kung saan ay ang positibong value. Ang dahilan dito ay dahil sa convention. Kung gusto nating tukuyin ang parehong positibo at negatibong square root, gagamit tayo ng ± (plus-minus sign).
Halimbawa:
* √9 = 3 (principal square root)
* Ang mga solution sa x² = 9 ay x = ±3
Ang parehong prinsipyo ay umaaplay sa iba pang even roots. Halimbawa, ang ⁴√16 = 2, dahil 2⁴ = 16. Ang -2 ay hindi itinuturing na solution sa ⁴√16 dahil ang convention ay tumutukoy sa principal (positive) root.
Paghahanap ng Domain ng Even Root Function:
Ang paghahanap ng domain ng even root function ay nangangailangan ng pagtukoy sa mga value ng x kung saan ang radicand ay non-negative. Ito ay dahil ang even root ng isang negatibong numero ay hindi defined sa set ng mga real numbers.
Narito ang mga hakbang para sa paghahanap ng domain:
1. Itakda ang Radicand na Mas Malaki sa o Katumbas ng Zero: Kung ang function ay f(x) = ⁿ√g(x), itakda ang g(x) ≥ 0.
2. Lutasin ang Inequality: Lutasin ang inequality para sa x. Ang solution set na ito ay ang domain ng function.
3. Ipahayag ang Domain sa Interval Notation: Isulat ang domain bilang isang interval, gamit ang brackets [ ] para isama ang mga endpoints at parentheses ( ) para hindi isama ang mga endpoints.
Mga Halimbawa ng Paghahanap ng Domain:
Halimbawa 1:
f(x) = √ (x - 3)
1. Itakda ang radicand na mas malaki sa o katumbas ng zero: x - 3 ≥ 0
2. Lutasin ang inequality: x ≥ 3
3. Ipahayag ang domain sa interval notation: [3, ∞)
Ito ay nangangahulugan na ang domain ng function na ito ay ang lahat ng real numbers na mas malaki sa o katumbas ng 3.
Halimbawa 2:
g(x) = ⁴√(5 - 2x)
1. Itakda ang radicand na mas malaki sa o katumbas ng zero: 5 - 2x ≥ 0
2. Lutasin ang inequality:
* -2x ≥ -5
* x ≤ 5/2 (Tandaan na binabaliktad natin ang inequality sign kapag nag-divide tayo sa negatibong numero)
3. Ipahayag ang domain sa interval notation: (-∞, 5/2]
Ito ay nangangahulugan na ang domain ng function na ito ay ang lahat ng real numbers na mas maliit sa o katumbas ng 5/2.
Halimbawa 3:
h(x) = √ (x² - 4)
1. Itakda ang radicand na mas malaki sa o katumbas ng zero: x² - 4 ≥ 0
2. Lutasin ang inequality:
* (x - 2)(x + 2) ≥ 0
* Ang critical values ay x = 2 at x = -2. Gagamit tayo ng sign chart para matukoy kung saan ang expression ay positive o zero.
| Interval | x < -2 | -2 < x < 2 | x > 2 |
|-------------|--------|-------------|-------|
| x - 2 | - | - | + |
| x + 2 | - | + | + |
| (x-2)(x+2) | + | - | + |
.jpg)
even root We celebrate women from all generations and all backgrounds and the tremendous impact they have in the United States, the Philippines, and around the world. “Maligayang .
even root - Finding Domain: Radical/Root Function (Even Root)